INTRAVENOUS GLUTATHIONE
Glutathione is a small molecule that acts as an antioxidant in the body. Antioxidants are substances that protect cells from damage caused by harmful molecules known as free radicals. Free radicals are produced as a byproduct of normal cellular processes, but they can also be generated by external factors such as exposure to radiation, pollutants, and toxic chemicals. If left unchecked, free radicals can damage cellular components such as DNA and proteins, leading to a range of health problems, including inflammation, aging, and disease.
Glutathione functions as an antioxidant by donating electrons to neutralize free radicals and prevent them from causing cellular damage. Additionally, glutathione can also regenerate other antioxidants, such as vitamins C and E, allowing them to continue to protect cells from damage.
The liver is one of the key organs that benefits from IV glutathione. This organ is responsible for detoxifying the body and removing harmful substances, including drugs, alcohol, and environmental toxins. Glutathione plays an important role in this process by binding to toxins and facilitating their elimination from the body. IV administration of glutathione can help to increase the liver's ability to detoxify harmful substances, leading to improved liver function.
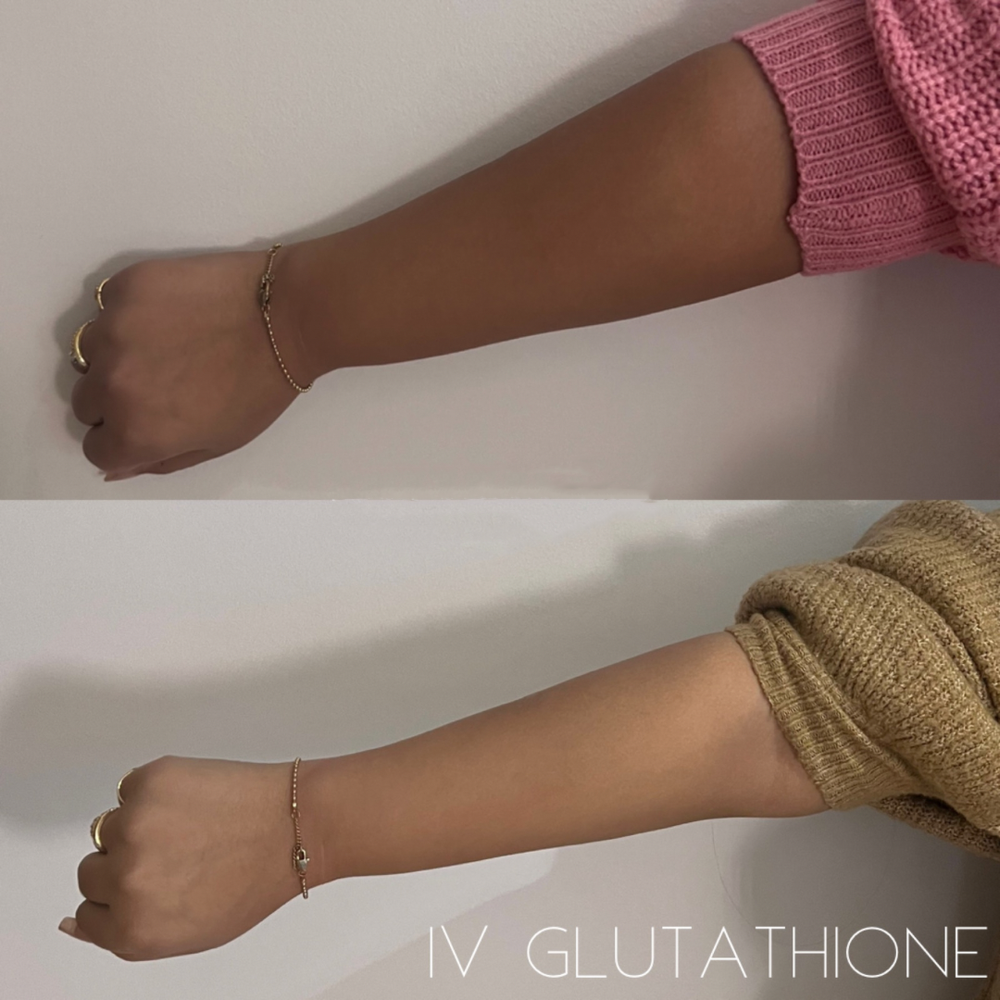
In addition to its beneficial effects on the liver, IV glutathione has also been shown to improve skin health. The skin is exposed to a variety of environmental insults on a daily basis, including UV radiation, pollutants, and toxic chemicals. These insults can generate harmful free radicals that can damage the skin and contribute to a range of skin problems, including aging, pigmentation, and wrinkles. Glutathione acts as an antioxidant in the skin, neutralizing free radicals and protecting the skin from damage. IV administration of glutathione has been shown to improve skin hydration, elasticity, and overall appearance, leading to a more youthful and radiant complexion.
How does IV Glutathione brighten skin?
Glutathione is thought to inhibit melanin production by interfering with the activity of an enzyme called tyrosinase, which is involved in the formation of melanin. Tyrosinase catalyzes the conversion of the amino acid tyrosine into melanin. Glutathione is believed to bind to tyrosinase, thereby reducing its activity and the amount of melanin that is produced.Glutathione is thought to inhibit melanin production by interfering with the activity of an enzyme called tyrosinase, which is involved in the formation of melanin. Tyrosinase catalyzes the conversion of the amino acid tyrosine into melanin. Glutathione is believed to bind to tyrosinase, thereby reducing its activity and the amount of melanin that is produced.